For this post, I am switching gears a little and sharing a ministry idea I have pursued with my church that helps young people understand God’s Word better by helping them visualize the world of the Bible. I know from my own experience growing up that many children (and even some adults like myself) struggle to learn through traditional, book-oriented resources often used in Bible classes and Sunday Schools. They would much rather being doing something active or watching a video, and this is not a bad thing, though it presents challenges for learning. To reach kids like this better and help them understand the world of the Bible, I have started what I call Bible Brick Club at our church for kids ages 8 to 12. We meet for 90 minutes and spend the first 20 minutes or so learning about a new Bible passage and the context in which it took place. I show them on a projector pictures of places and objects connected with the passage, such as the city of Jerusalem during New Testament times and pictures of what the Temple probably looked like. Then we spend most of the rest of the time working together to recreate the scene with LEGOs (or any LEGO-compatible bricks). I think it has proven to be very fun and effective for learning, as long as you are willing to have Jar Jar Binks show up in Jerusalem now and then or for characters to be mining gold on the backside of the Mount of Olives. For one of our projects, we spent three sessions building a replica of Jerusalem, complete with pools where Jesus performed miracles, the Garden of Gethsemane, and Golgotha. Each time we met we reviewed what happened at each place we had built so far, and this seemed to help cement the stories in their minds. And at the very minimum, the kids seemed to have a good time learning about the Bible at church, which I say is a win all by itself. As far as materials and preparation, the biggest challenge for us was getting enough LEGOs for the group, so I would start early collecting those. We invited donations of used LEGOs, too, but I quickly found out that not many people are willing to part with their own LEGOs! Another spinoff of this idea (though I have not attempted it yet), is to assemble a virtual team of older kids (perhaps ages 12-15) to recreate Bible scenes together using Minecraft. I hope some of you are able to use this idea in your own ministry at church, at school, at community centers, etc. If you do, I would love to hear about it (see my contact info here).
Jesus Speaks with a Woman in Samaria
John 4
As the story of Jesus’ encounter with a Samaritan woman demonstrates, even simple geography–the divine arrangement of places where God leads us in life–can position us for fruitful ministry if we are willing to reach out to those along our journey. This episode in Jesus’ ministry occurred immediately after Jesus had cleared the Temple in Jerusalem and was gaining even more followers than John the Baptist (John 2:13-25; 4:1-3). Likely wanting to avoid a direct clash with Jewish leadership so early in his ministry, Jesus chose instead to return to Galilee. The most direct route from Jerusalem to Galilee passed through Samaria, and, as the Jewish historian Josephus notes, this was the route normally chosen by most Jews at the time (Antiquities of the Jews, Book XX:6). The city of Samaria (renamed Sebaste by Jesus’ time) was originally the capital of the northern kingdom of Israel, but in 722 B.C. the Assyrians exiled many Israelites to other parts of their empire and relocated other foreign peoples in Israel (2 Kings 15:29; 17:1-24; 1 Chronicles 5:26; also see “Israelites Are Exiled to Assyria”). This diverse population then developed a new religion that mixed elements of Israelite worship with pagan worship (2 Kings 17:24-41), and centuries later they set up their own temple on Mount Gerizim. Because of their mixed ancestry and religion, Samaritans were often detested by many Jews (John 4:9), and hostilities periodically erupted between Jews and Samaritans. Jesus himself would later be refused entry into Samaria while traveling from Galilee to Jerusalem (Luke 9:52-56; also see “Jesus’ Final Journey to Jerusalem”), and Josephus notes that about 20 years after this time a number of Galileans were killed by Samaritans as they attempted to make their way to Jerusalem through the village of Ginae. Probably because of these hostilities, some Jews preferred to take alternate routes that bypassed Samaria. Still other Jews chose these routes to avoid even associating with Samaritans. Jesus, however, appears to have chosen the more direct route through Samaria, which led him to the village of Sychar–right next to the ancient site of Shechem and Mount Gerizim. There he met a Samaritan woman by a well and spoke to her about God’s gift of living water for her soul. He also revealed supernatural knowledge about her, so she asked him whether Mount Gerizim or Jerusalem was the proper place to worship. Jesus gently rebuked her belief in Samaritan worship practices, but he also assured her that one day the physical location of worshipers will no longer matter. Instead, all true believers will worship God in spirit and truth. When Jesus revealed to the woman that he was the Messiah, she left her water jar and told the townspeople about Jesus. Meanwhile, Jesus’ disciples returned, and Jesus urged them to recognize that the fields were ripe for harvesting, presumably meaning that many Samaritans were ready to believe in him. Because of the Samaritan woman’s testimony, many of the townspeople believed in Jesus and persuaded him to stay there two more days before returning to Galilee. Years later the apostle Philip found fruitful ministry among the Samaritans as well, and many came to faith in Jesus (Acts 8:5-13; also see “The Ministries of Philip and Peter”).

⤓ download hi-res file 🔍 see in TimeGlider
Resurgence of Israel and Judah
2 Kings 14:23-29; 15:1-7; 2 Chronicles 26
The long, concurrent reigns of Jeroboam II of Israel and Uzziah (also called Azariah) of Judah marked a period of resurgence after their nations had suffered nearly sixty years of decline and unrest. By the time both kings ascended to the throne in 793 B.C. and 792 B.C., Moab had revolted from Israel and seized land belonging to the tribe of Reuben (2 Kings 1:1; see “The Nation of Moab and the Tribe of Reuben”), and Edom and Libnah had revolted from Judah (2 Kings 8:16-24; 2 Chronicles 21:1-11; see “Edom and Libnah Revolt”). Jehu then brutally overthrew Ahab’s dynasty, but he later suffered the loss of all Gilead to the rising power of Aram (2 Kings 1:1; 3:1-27; 8:12; 10:32-33; 2 Chronicles 21:8-10; see “Aram Captures Gilead”). Soon after this, however, the Assyrian king Adad-nirari III (who may be the “savior” of 2 Kings 13:5) attacked Aram, but then he withdrew, thus creating a power vacuum to the north. Jeroboam of Israel took advantage of this opportunity and captured much of Aram, though it is unclear how firmly he held Aram or for how long. During this same time, king Uzziah of Judah captured the Red Sea port city of Elath in the far south, which belonged to Edom, and he also attacked the Arabs of Gur, who were likely located nearby. He also attacked the Meunites who lived in Seir, the formerly Edomite region south of the Judean Negev, though the Meunites themselves do not appear to have been Edomites. The Meunites are probably the same as the “Maonites” mentioned in Judges 10:12, and they also joined the Moabite alliance that attacked king Jehoshaphat of Judah (2 Chronicles 20). About a century after Uzziah’s time, during the reign of Hezekiah, some Simeonites attacked some Meunites in the Negev and seized their land (1 Chronicles 4:41-43). According to the Septuagint, the Meunites also paid Uzziah tribute (2 Chronicles 26:7-8), and Uzziah likely captured some of the Meunites and gave them as servants for the Temple of the Lord, which appears to have been a common practice in Israel since the time of Moses and Joshua (see Numbers 31:30; Joshua 9:27; Ezra 8:20). Their descendants are listed among the “Nethinim,” who served at the Temple during time of Ezra and Nehemiah (Ezra 2:50; Nehemiah 7:52). Uzziah also attacked the Philistine cities of Gath, Ashdod, and Jabneh and established other cities throughout Philistia. He built towers in Jerusalem at the Corner Gate, the Valley Gate, and the Angle as well as towers in the wilderness. He also dug many cisterns to store water for his large herds, both in the Shephelah (the foothills near Gath) and in the plain. He also had large farms and vineyards and strengthened Judah’s army. As far as moral leadership, the writer of Kings deems Jeroboam as a bad king for allowing idolatry to continue in Israel, but Uzziah is deemed as good, though he later sinned and was afflicted with leprosy for making an offering on the altar of incense.

⤓ download hi-res file 🔍 see in TimeGlider
Solomon’s International Presence
1 Kings 9-10; 2 Chronicles 2:1-18; 8:1-9:28
Near the beginning of Solomon’s reign, the Lord promised to bless him with great wisdom, riches, and honor (1 Kings 3:2-15), and the fulfillment of this promise led to great fame for Solomon throughout the Near East. Humanly speaking, Solomon had been set up for immense success by his father David, who passed on to him a powerful kingdom that stretched from the tip of the Red Sea to the Euphrates River (2 Samuel 8-10; 1 Chronicles 18-19; 2 Chronicles 8). During Solomon’s reign Israel controlled all land routes leading from Egypt and the Red Sea to the Aramean and Hittite nations to the north, and they also controlled the northern terminus of the great Incense Route leading from the peoples of southwest Arabia to the shores of the Mediterranean Sea at Gaza. Solomon appears to have capitalized on his strategic control over travel and shipping throughout the region by setting up a very lucrative international arms dealership, through which he paired chariots bought from Egypt with horses bought from Kue (the term sometimes translated as “Egypt” should probably be translated “Muzur,” a district near Kue) and sold them to the kings of the Hittites and Arameans. Solomon also likely gained immense wealth from very productive copper mines at Punon, Timna, and elsewhere (see “Southern Arabah Valley” map). All this won him great renown among all the rulers of the Near East, including the queen of Sheba, who traveled over a thousand miles to see for herself Solomon’s great wisdom and splendor. She brought with her luxurious gifts from her land, including spices, precious stones, and gold, which she may have obtained from nearby Ophir. Solomon also arranged for King Hiram of Tyre to provide him with cedar timbers from Lebanon to build the Temple of the Lord and his royal palace (2 Chronicles 2). The logs were bound into rafts, floated down to Joppa, and then disassembled and hauled up to Jerusalem. Solomon also launched ships to sail to faraway lands during his reign and bring back riches and exotic goods. Scholars have proposed various locations for the exact destination of the ships, and some have struggled to reconcile what can seem like confusion on the part of the biblical writers over the term Tarshish. But a careful reading of the biblical accounts indicates that there were probably two separate fleets of ships: the fleet of Hiram and Solomon’s fleet of ships of Tarshish. Both fleets are separately mentioned in 1 Kings 10:22, and the phrase “at sea with” may simply indicate that they were sailing at the same time but not necessarily together. Also, the list of goods brought back by Hiram’s fleet is somewhat different than the list of goods brought back by Solomon’s fleet (compare 1 Kings 10:11, 22; 2 Chronicles 8:17-18; 9:10, 21). Likewise, the wording of 2 Chronicles 8:17-18 is that Hiram “sent to [Solomon] by the hand of his servants ships and servants familiar with the sea,” but the implication seems to be that the ships remained Hiram’s, not Solomon’s, whereas the other fleet of ships of Tarshish appears to have belonged to Solomon, though the ships were manned by Hiram’s men as well (2 Chronicles 9:21). Thus, Hiram’s fleet set sail from Ezion-geber, traveled the length of the Red Sea, and acquired gold from Ophir. Solomon’s fleet, on the other hand, could have sailed either the Red Sea or the Mediterranean Sea, since the term ships of Tarshish seems to have been used at times to indicate a class of trading or refinery ships rather than a specific destination (see article for “Tarshish” map). It is also possible, however, that the term Tarshish referred to the ships’ actual destination, which during Solomon’s reign appears to have been located in the far western Mediterranean Sea. This is supported by isotopic studies of silver found in Israel during Solomon’s time, which have traced the source to Tharros on the island of Sardinia. This also fits well with the length of time given for the voyage of Solomon’s fleet, which returned every three years with their exotic goods.

⤓ download hi-res file 🔍 see in TimeGlider
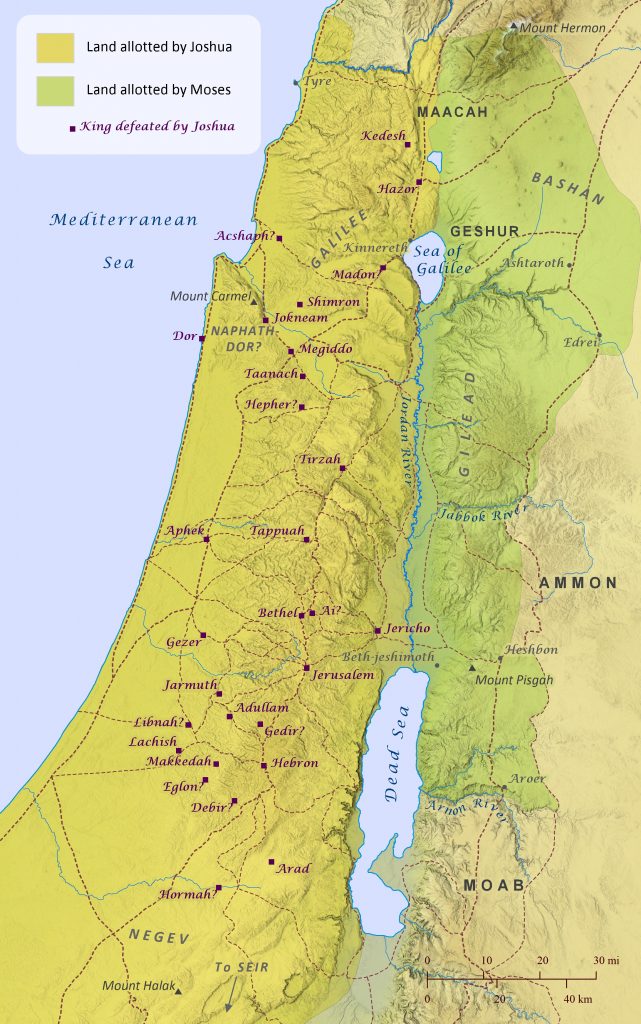
Kings Defeated by Joshua
Joshua 12:7-24
The first half of the book of Joshua recounts the many battles fought during the conquest of the Promised Land. At the very end of this account, Israel’s conquests are summarized in a list of kings defeated by Moses and Joshua. Moses’ victories in the Transjordan are listed first, followed by Joshua’s victories in the land west of the Jordan River. Each of these defeated kings ruled over a single city-state (and sometimes its surrounding territory), and the cities listed were scattered throughout the entire land allotted to the Israelites by Moses and Joshua. It appears, however, that Israel was not always able to maintain control over some of the cities that were defeated, for several of them are noted as the headquarters of various rulers who oppressed the Israelites during the period of the Judges (e.g., Jerusalem, Gezer, Taanach, Dor, Megiddo, and Hazor; see Judges 1-4).